Toxic air returns to Delhi — explore the reasons behind persistent pollution and why tackling it remains a challenge.
Delhi’s air quality has deteriorated to hazardous levels once again, with the Air Quality Index (AQI) reaching over 500 in several areas, far exceeding the World Health Organization’s safe limit of 10 µg/m³ for PM2.5. This recurring crisis, particularly acute during the winter months, has significant health implications and underscores the complexities involved in combating air pollution in the capital.
Key Contributors to Delhi’s Air Pollution
- Vehicular Emissions: Delhi’s roads are congested with over 10 million vehicles, many of which are older models emitting high levels of nitrogen oxides and fine particulate matter.
- Construction Activities: Ongoing urban development projects generate substantial dust, especially during dry months, contributing significantly to airborne pollutants.
- Industrial Emissions: Factories and power plants in and around Delhi release pollutants like sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and particulate matter into the atmosphere, worsening air quality.
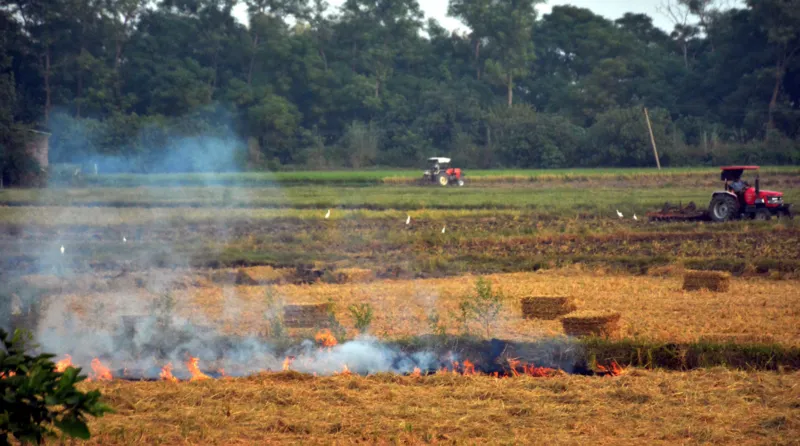
- Stubble Burning: Farmers in neighboring states like Punjab and Haryana burn crop residue to clear fields, releasing massive amounts of smoke and harmful particles into the air, which are then carried into Delhi by winds.
- Firecrackers During Festivals: Despite bans, the use of firecrackers during festivals like Diwali adds to pollution levels, further worsening air quality.
Health Impacts of Air Pollution

Air pollution in Delhi poses significant health risks, including:
- Respiratory Issues: Increased cases of asthma, bronchitis, and other chronic lung diseases.
- Cardiovascular Problems: Long-term exposure can lead to heart diseases.
- Cognitive Decline: Studies have linked prolonged exposure to reduced lung function and premature death, especially in children, the elderly, and people with compromised immune systems.
- Mental Health Effects: Air pollution has been associated with increased risks of stroke, cognitive decline, and pregnancy complications, including low birth weight.
Challenges in Combating Air Pollution
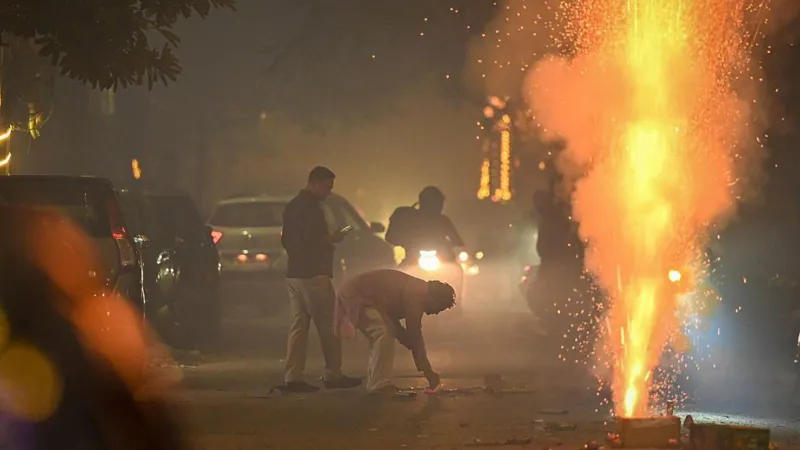
Several factors complicate efforts to improve Delhi’s air quality:
- Population Growth: Delhi’s population exceeds 20 million, leading to increased vehicular emissions, construction dust, and energy consumption.
- Industrial Growth: Rapid urbanization and industrialization contribute to higher pollution levels.
- Weather Conditions: During the winter months, cooler air traps pollutants close to the ground, forming a thick layer of smog that blankets the city.
- Regulatory Challenges: Despite existing regulations, enforcement remains inconsistent, and violations are common.
Proposed Solutions
To address Delhi’s air pollution crisis, experts suggest:
- Transitioning to Cleaner Energy Sources: Shifting from coal-based power plants to renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
- Promoting Electric Vehicles: Encouraging the use of electric vehicles to reduce emissions from transportation.
- Enhancing Public Transportation: Expanding and improving public transport systems to reduce the number of private vehicles on the road.
- Implementing Strict Emission Standards: Enforcing stricter emission standards for industries and vehicles.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public about the health risks of air pollution and ways to reduce exposure.
Conclusion
Delhi’s recurring air pollution crisis is a multifaceted issue that requires coordinated efforts from the government, industries, and citizens. While challenges persist, implementing comprehensive strategies can lead to significant improvements in air quality and public health.
Also Read : Ram Charan and Upasana Konidela expecting 2nd baby, she shares video from baby shower: ‘Double the love’















 Categories
Categories